As we enter 2025, what automation testing trends will shape the future?
Additionally, developments in one year tend to establish the trends for the following year. (Some trends I pointed out from 2024 will also continue in 2025)
Money invested in companies is a key indicator that often signals a trend.
Read to the end because you won’t believe #12!
With that in mind, I have compiled my list of the top automation testing trends for 2025, using the above criteria, just as I have been doing for the past 13 years.
Key Takeaways:
- The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in automation testing is expected to increase, enabling more efficient and accurate testing.
- The shift-left testing trend involves finding bugs earlier and more cost-effectively by executing more automated tests against code changes in the CI/CD pipeline, rather than just in pre-production.
- The rise of testing in production to validate features at a real production scale with millions of users
The first one is obvious, so let’s get it out of the way.
1. AI-Assisted Testing Boom Continues
AI and machine learning will become even more integral to helping you boost your testing efficiency.
Are any testers using AI to help with testing now?
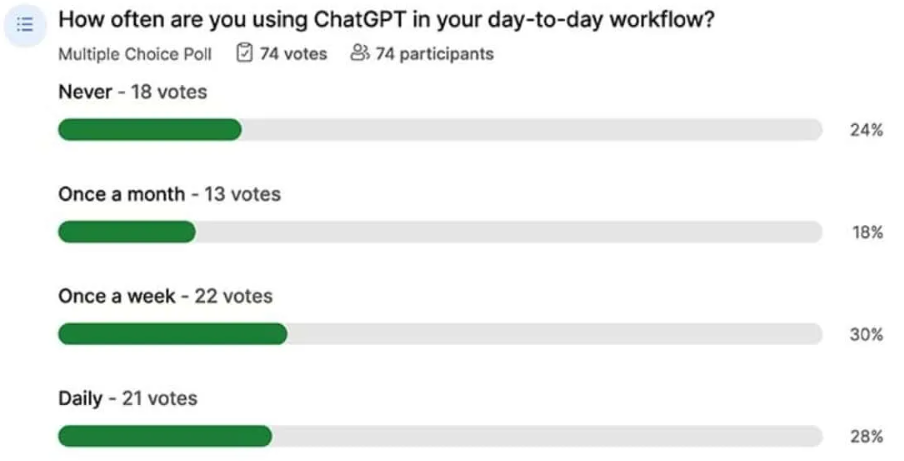
Surprisingly, based on surveys like those from LambdaTest and The TestGuild webinar polls, most testers have already incorporated AI into their workflows. (So if you’re not experimenting with AI, you are already behind)
A recent Lambda Test survey found AI Adoption among Software Testers at 78%.
In a TestGuild Webinar on Generative AI, 76% of testers say they already use (or plan on using) Chat-GPT AI to help them with their day-to-day testing activities.
However, remember that real software testing requires a deep understanding of the software being tested. However, it does not rule out AI assistance with many testing activities:
- Automated Test Case Generation: AI algorithms can analyze requirements, user stories, and application changes to design optimal test cases that target key use cases, thereby maximizing coverage.
- Intelligent Test Data Creation: Generating high-quality, realistic test data at scale remains a significant bottleneck. However, AI/ML techniques, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs), show promise for efficiently synthesizing production-grade test datasets, thereby achieving more excellent test coverage. The capabilities of GANs are impressive for data augmentation, as they can effectively learn the underlying distribution of the input data and generate highly realistic samples. However, once again, you need a tester to evaluate the quality of the generated sample.
- Predictive Defect Models: AI/ML models will be trained on historical defects and releases to predict the types of bugs likely to manifest and identify high-risk areas of the code, guiding test targeting for maximum effectiveness.
- Test Optimization and Prioritization: By assessing business risk, use cases, and development activity, ML will intelligently guide test case prioritization and coverage for each release and code change, allocating testing resources to the highest-value areas.
- Automated Root Cause Analysis: Once bugs surface, AI will analyze logged telemetry across the entire integrated architecture to rapidly and automatically pinpoint the likely root causes of software failures. (This is an area where Guild members say they struggle)
Once again, all these activities require a human tester to ensure the AI-generated data is accurate.
Follow the money in 2024 (key trend indicator):
- Perforce released “Test Data Pro by BlazeMeter,” which leverages generative AI technology to simplify and enhance test data creation.
- Katalon announced TrueTest, an automated regression testing solution leveraging AI to generate and maintain regression tests by monitoring user activity.
- Integrated GenAI into TestResults.io to Create Test Cases
Multimodal AI Takes Automation to the Next Level
Plus, with the recent release of multimodal AI Google’s Gemini, AI in Testing will get even more interesting.
If you haven’t heard, Multimodal AI incorporates multiple data types, such as text, images, speech, and sensor inputs, processed via different algorithms to enable more flexible automated testing capabilities.
This is cool because this should allow multimodal AI to enhance test automation with things like:
- Visual Application Validation: Test bots utilize computer vision in conjunction with text processing to navigate and validate graphical interfaces, much like a human tester would, for enhanced coverage.
- Expanded Types of Testable Applications: The ability to interpret images, video, speech, and other signals enables test automation to cover a wider variety of applications beyond traditional web applications.
- Training with Diverse Sensory Inputs: Leveraging image, voice, and other multimodal inputs to train automated testing models leads to a more nuanced understanding of system behavior and defects.
- Mainstream Accessibility Integration of advanced multimodal frameworks like GPT-4 Turbo into commercial test tools makes these innovations accessible to non-specialized test teams.
By combining multiple data types processed through specialized algorithms tailored to each input, multimodal AI will deliver more comprehensive test automation capabilities, helping to mirror the complexity of real-world scenarios.
Is AI perfect? NO! Is it a silver bullet? NO!
However, it cannot be ignored and is highly beneficial when used correctly; it is only improving with time.
We have a bunch of sessions at this year's online Automation Guild design specifically to help automation engineers with AI, like:
- A Practical Guide To AI: How to Improve Quality In Software Development
- From Code to Cognition: The Journey Of AI And Automation
2. Testing For Low-Code/No-Code Apps
By 2025, surveys have shown that 70% of newly developed applications will use low-code or no-code technology, up from less than 25% in 2020.
As a result, testing needs will grow exponentially as the adoption of low-code/no-code app development increases across companies. Demand will surge for optimized, automated testing solutions tailored for low-code platforms.
Low-code/no-code application development platforms enable the faster delivery of apps with minimal manual coding. As more companies adopt these to empower business users and accelerate digital initiatives, testing needs grow exponentially.
Key aspects to testing low-code apps:
- E2E Testing: Low-code apps often support multiple channels, including web, mobile, and others, that require automated testing across various surfaces.
- Integration Testing Challenges: Connecting low-code apps to existing systems requires API and integration testing for end-to-end flows.
- Enabling Non-Technical Users: Allowing business teams that own low-code apps to execute tests without requiring deep technical expertise is crucial for adoption.
- Optimized CI/CD Pipeline Integration: Testing solutions must be embedded efficiently into continuous delivery pipelines favored by low-code platforms.
- Scalability Across App Portfolios: Testing capabilities must economically scale across large portfolios of low-code apps as adoption spreads enterprise-wide.
Follow the money in 2023 (key trend indicator):
- UIPath’s business automation platform recently added integration of new generative artificial intelligence, specialized AI and automation capabilities that will make it simple to automate almost any business task using natural language.
- Applitools announced its acquisition of Preflight, a leading low-code test automation platform.
3. End-to-end API Testing Automation
As you know, APIs serve as the connectivity fabric across systems in modern microservices architectures.
As API usage continues to multiply, automated API testing capabilities will need to expand in 2025 to validate functionality, performance, and security in pre-production environments.
Key aspects of robust API testing automation needed in 2025 include:
- Functional Validation: Verify APIs correctly implement required operations and business logic through extensive parameterized test cases.
- Load & Performance Testing: Execute high-volume test loads against APIs to uncover latency, bottlenecks, or errors under load using realistic scenarios.
- Security Testing: Validate APIs to resist OWASP top threats like injection attacks, broken authentication, rate limiting, and input filtering using negative test cases.
- Contract Validation: Compare API responses against OpenAPI or Swagger schemas to ensure compliance with defined contracts.
- Service Virtualization: Simulate APIs not yet developed or mock external-facing APIs to enable earlier testing before availability.
Leading API testing platforms and tools, such as Karate, Postman, Parasoft, and Tricentis, provide test automation capabilities, including auto-generated test cases. Additionally, tools like Cypress and Playwright are expected to see increased adoption for API Testing.
Some sessions at AG24 to help you learn more about API Testing for 2025:
- API Automation Mastery: From Novice To Ninja
- Accelerating API Testing: A Practical Guide to Automation with Cypress
- Mocking The Unmockable: Elevating Test Automation Stability Through Advanced API Simulation
- Safeguarding Digital Assets: Uncovering Security Risks In APIs