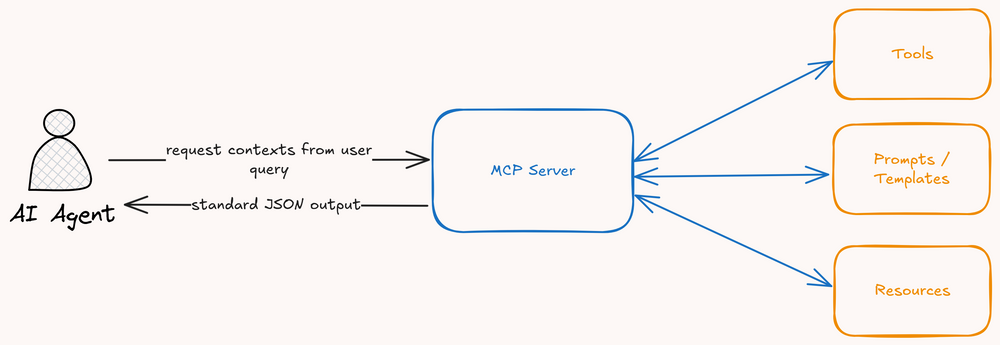
What is MCP?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open protocol developed by Anthropic that enables AI models like Claude to connect and interact with external applications, services, and data sources in a standardized way. Instead of writing custom integration code for each application, MCP provides a unified approach for AI to communicate with different tools.
Why MCP Matters
- Standardized Communication: A single protocol for all applications
- Easy Extensibility: Add new features without rewriting code
- Security: Clear access control mechanisms
- Reusability: One MCP server can be used by multiple AI clients
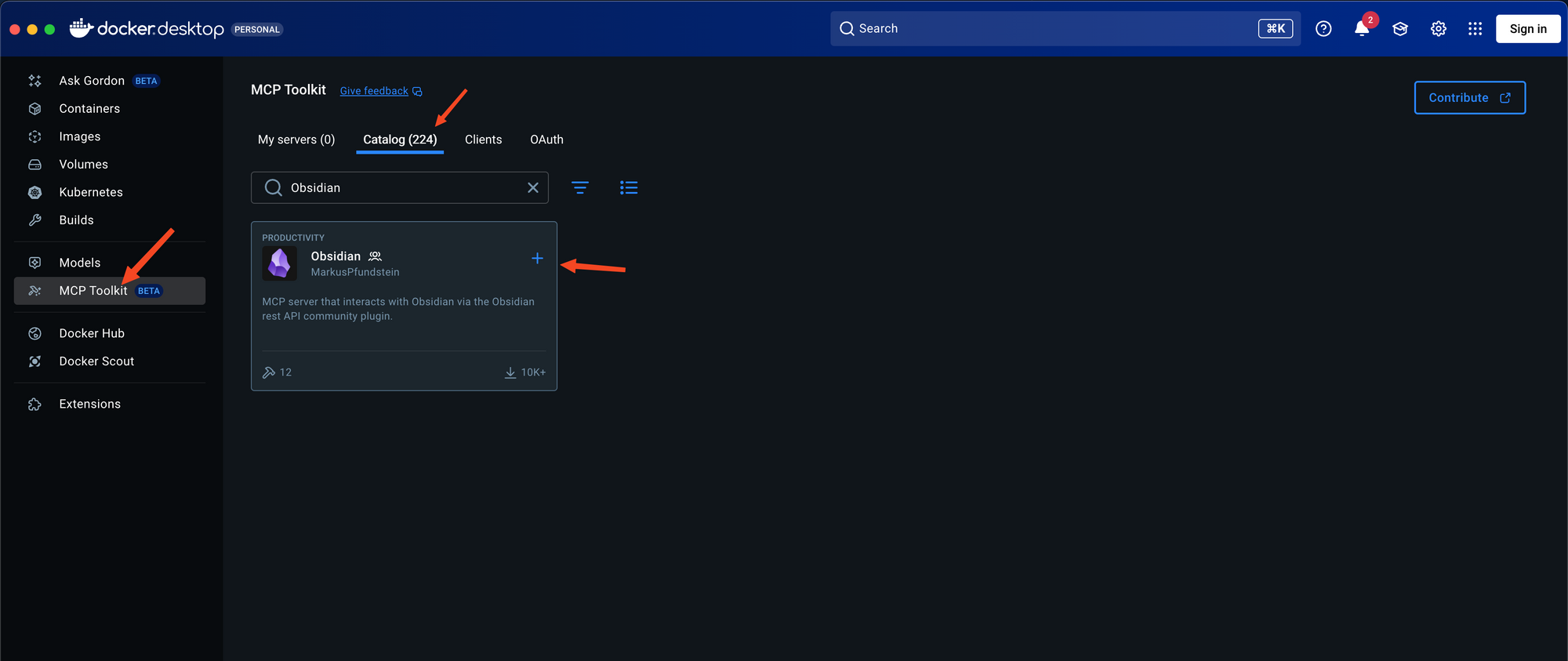
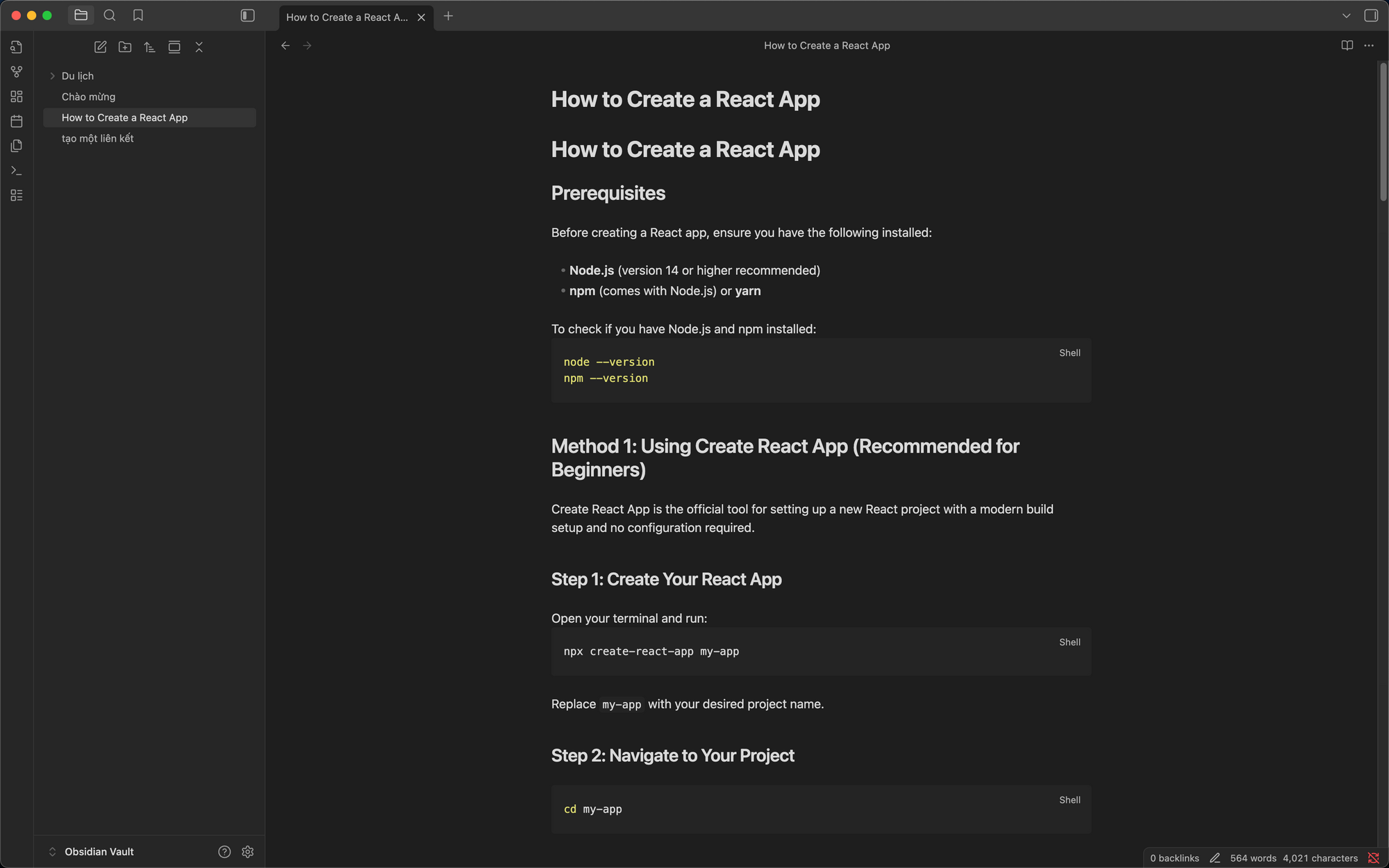
Step 1: Install MCP Server from Docker Desktop
- Select the MCP Toolkit and select the Catalog tab, find the MCP server, and select Add
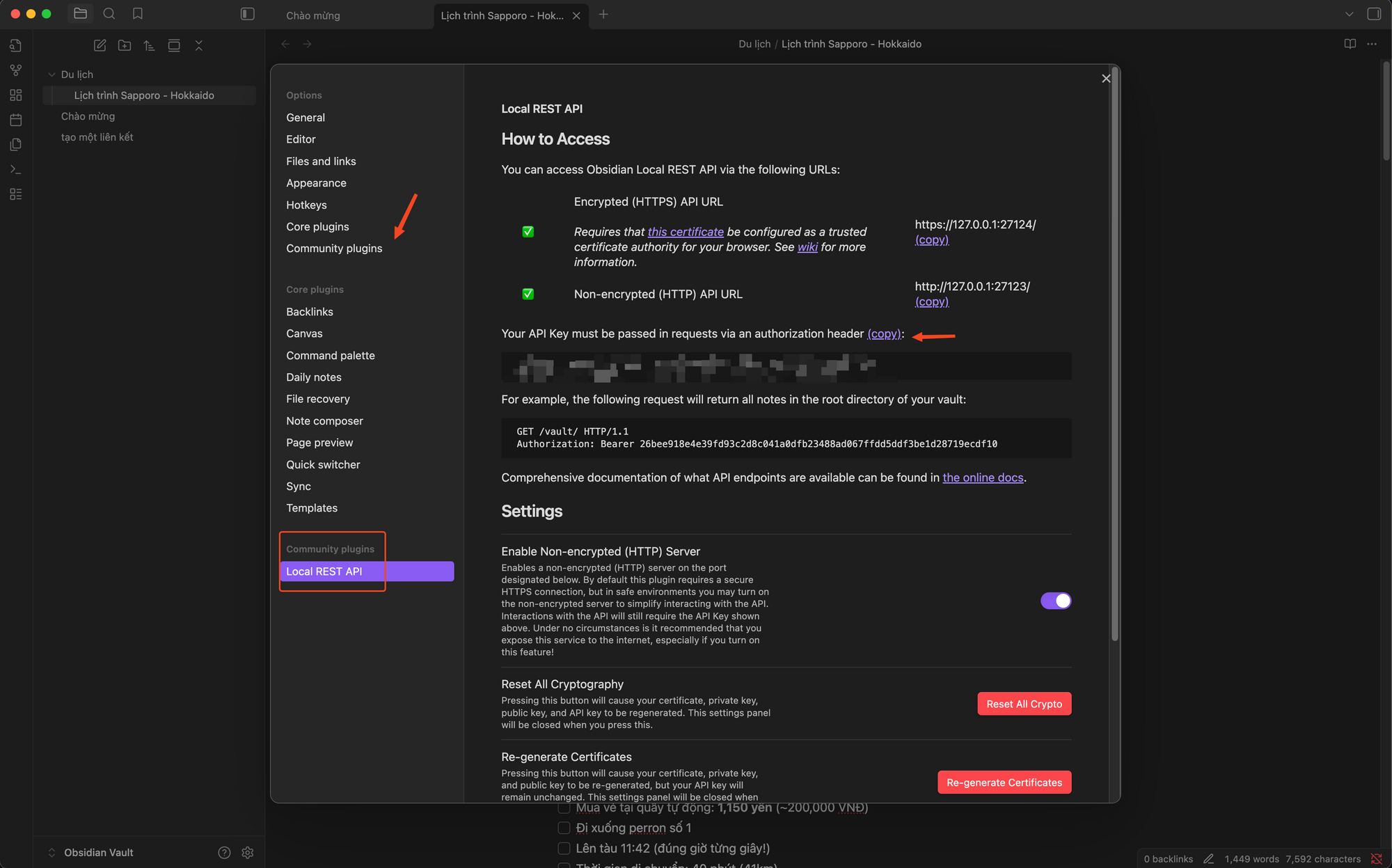
2. Open Obsidian and install the Local REST API plugin from the Community plugins, copy the Secret key
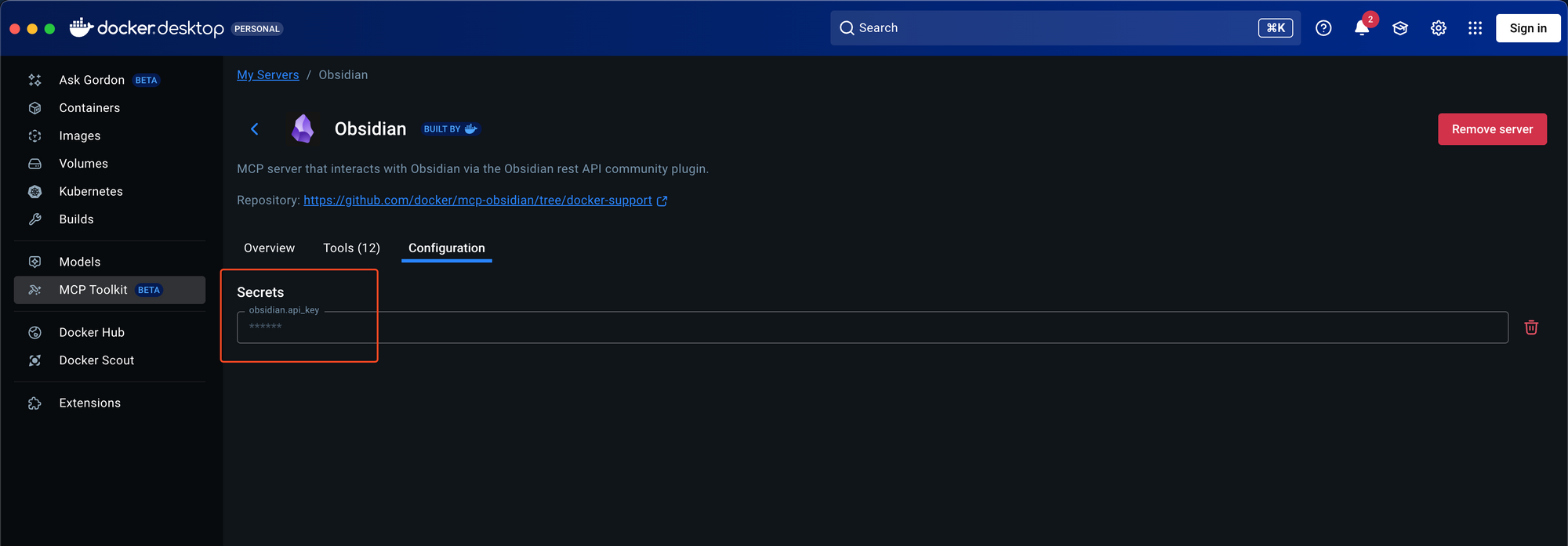
3. Provide the Secret key to the Obsidian MCP server and save
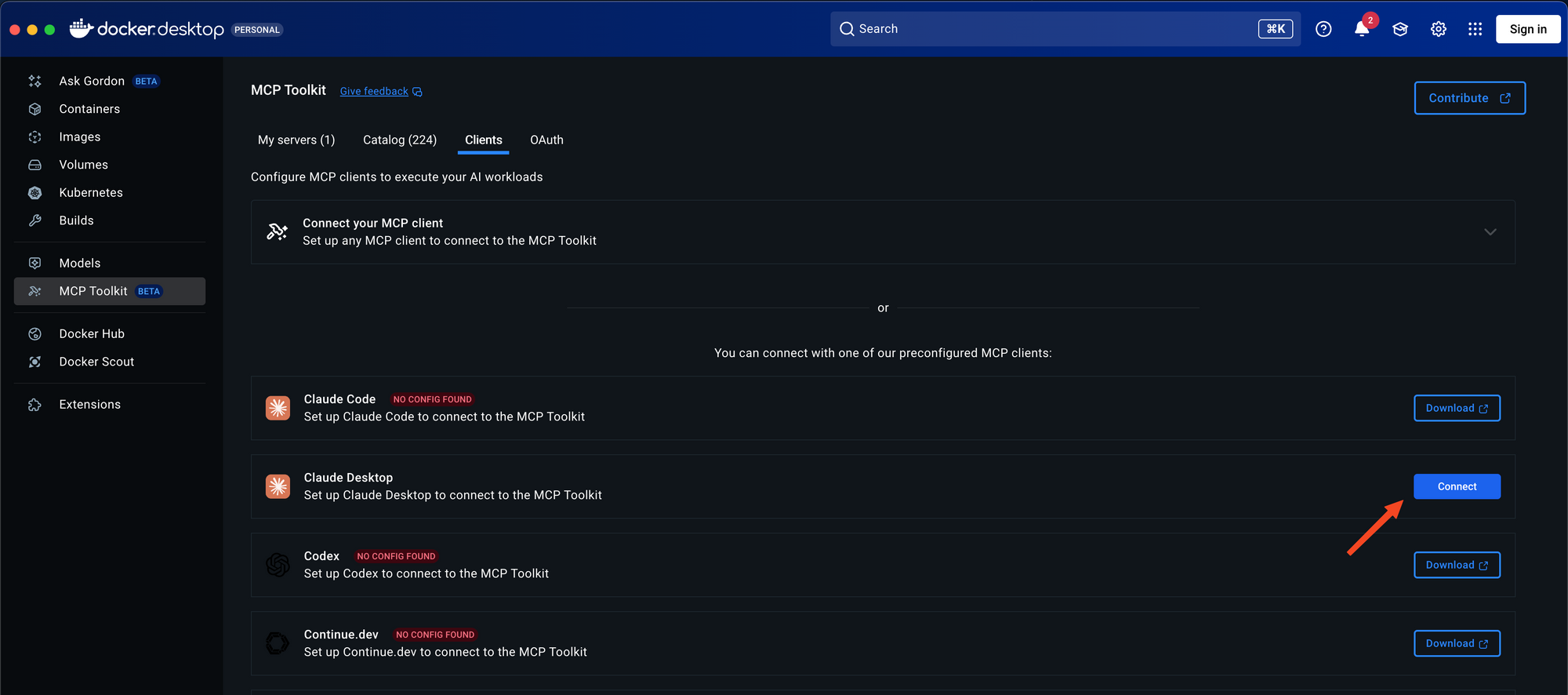
Step 2: Connect to Claude Desktop
Step 3: Restart and Test
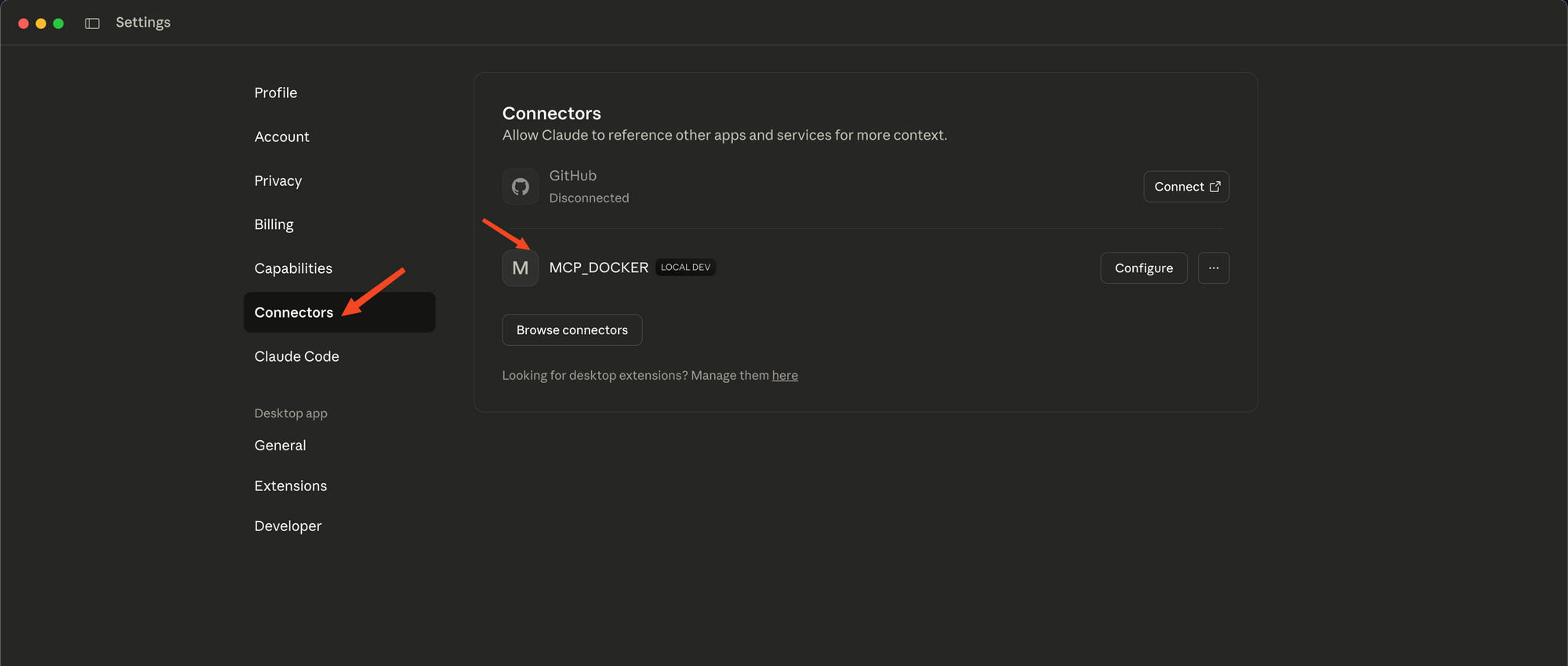
3.1. Restart Claude Desktop
Completely close Claude Desktop app and re-open it
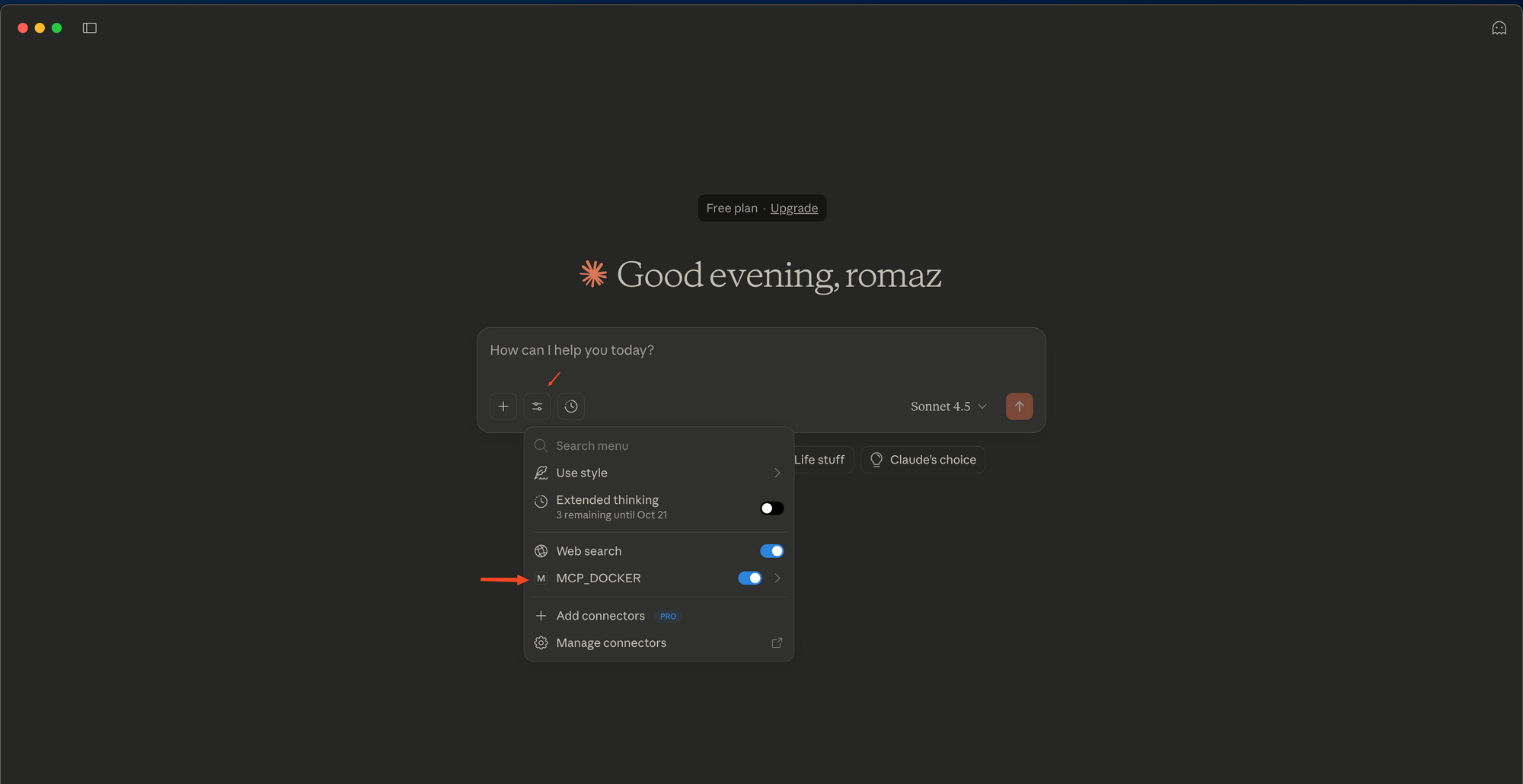
3.2. Verify Connection
In Claude Desktop, you should see a small icon (typically a hammer ? or plug ?) at the bottom left of the chat box, indicating that MCP tools are activated.
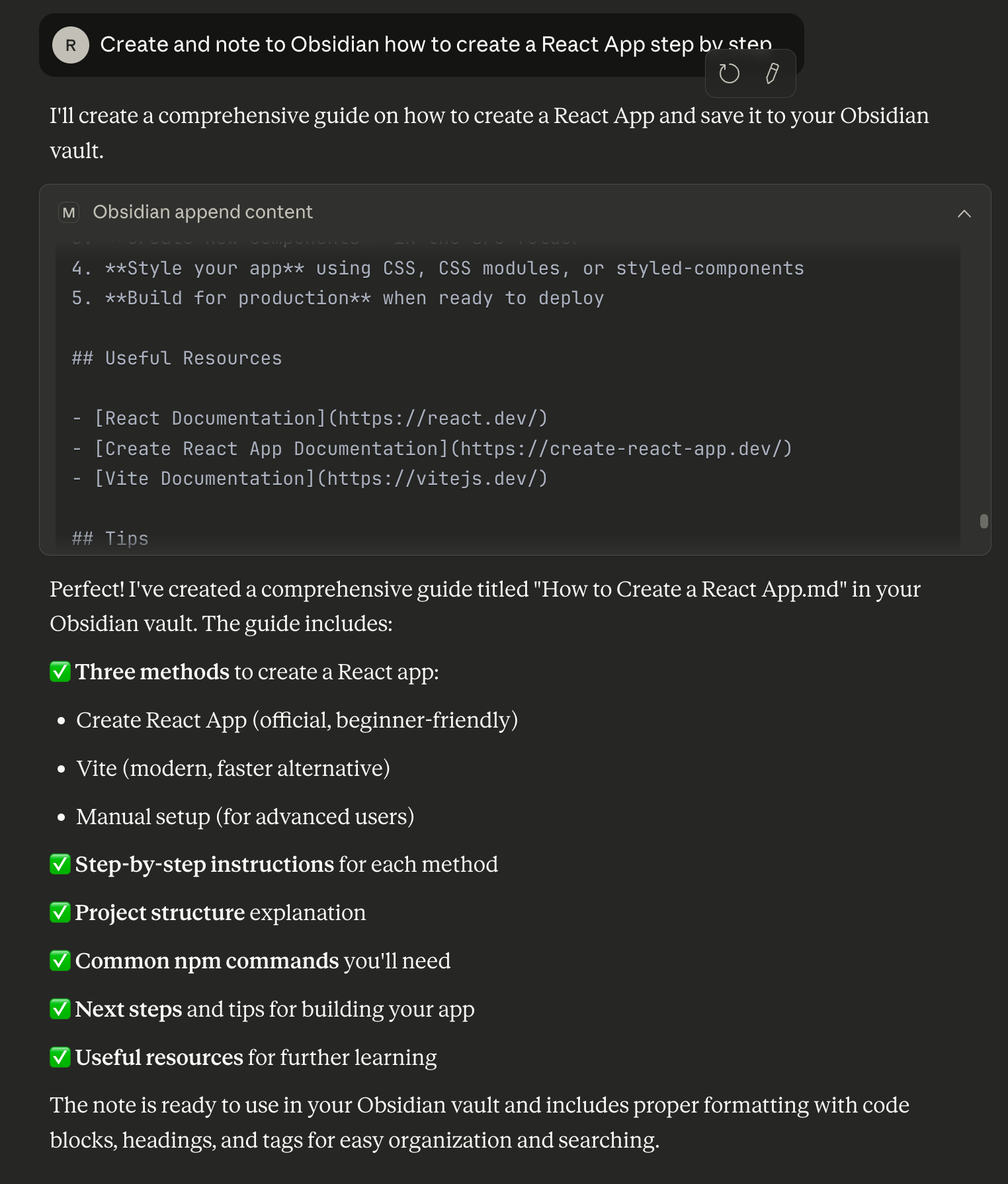
3.3. Test the Integration
Benefits of Using Docker Desktop Catalog
✅ Simplest approach: No code or complex configuration needed
✅ Auto-updates: Docker Desktop manages updates
✅ User-friendly GUI: Manage MCP servers through interface
✅ Pre-configured: Already tested and optimized
✅ One-click installation: Setup in minutes
Architecture Overview
┌─────────────────┐
│ Claude Desktop │
│ (MCP Client) │
└────────┬────────┘
│ stdio
│
┌────────▼─────────┐
│ Docker Desktop │
│ MCP Container │
└────────┬─────────┘
│ file system
│
┌────────▼─────────┐
│ Obsidian Vault │
│ (Markdown files) │
└──────────────────┘How It Works
1. Tool Discovery
Claude Desktop queries the MCP server for available tools via the tools/list method.
2. Tool Invocation
When you ask Claude to create a note, it calls the MCP server using tools/call with appropriate parameters.
3. File Operations
The MCP server performs file system operations (create, read, update) on the Obsidian vault.
4. Response
Results are returned to Claude, which then communicates them back to you in natural language.
Security Considerations
- The MCP server only has access to the mounted vault directory
- All operations are logged in Docker container logs
- You can stop the container anytime to revoke access
- File permissions are inherited from the host system
Performance Tips
- Keep vault size reasonable (< 10,000 notes) for faster searches
- Use folder organization for better file management
- Regular cleanup of unused notes
- Monitor Docker container resources in Docker Desktop
Conclusion
Using MCP from Docker Desktop Catalog is the fastest and simplest way to get started with MCP and Obsidian.
You now have an AI assistant that can write directly to your Obsidian vault! ??
Next Steps
- Explore other MCP servers in Docker Desktop Catalog
- Create custom templates for different note types
- Integrate with other tools (calendar, task management)
- Build automation workflows with multiple MCP servers