What is Revit API?
Revit API is a set of tools that lets you programmatically interact with Autodesk Revit. It allows you to create plugins, automate repetitive tasks, and add custom features to fit your design needs. In short, Revit API helps you customize Revit and make it more powerful for your workflow.
Understanding the Architecture of Revit API
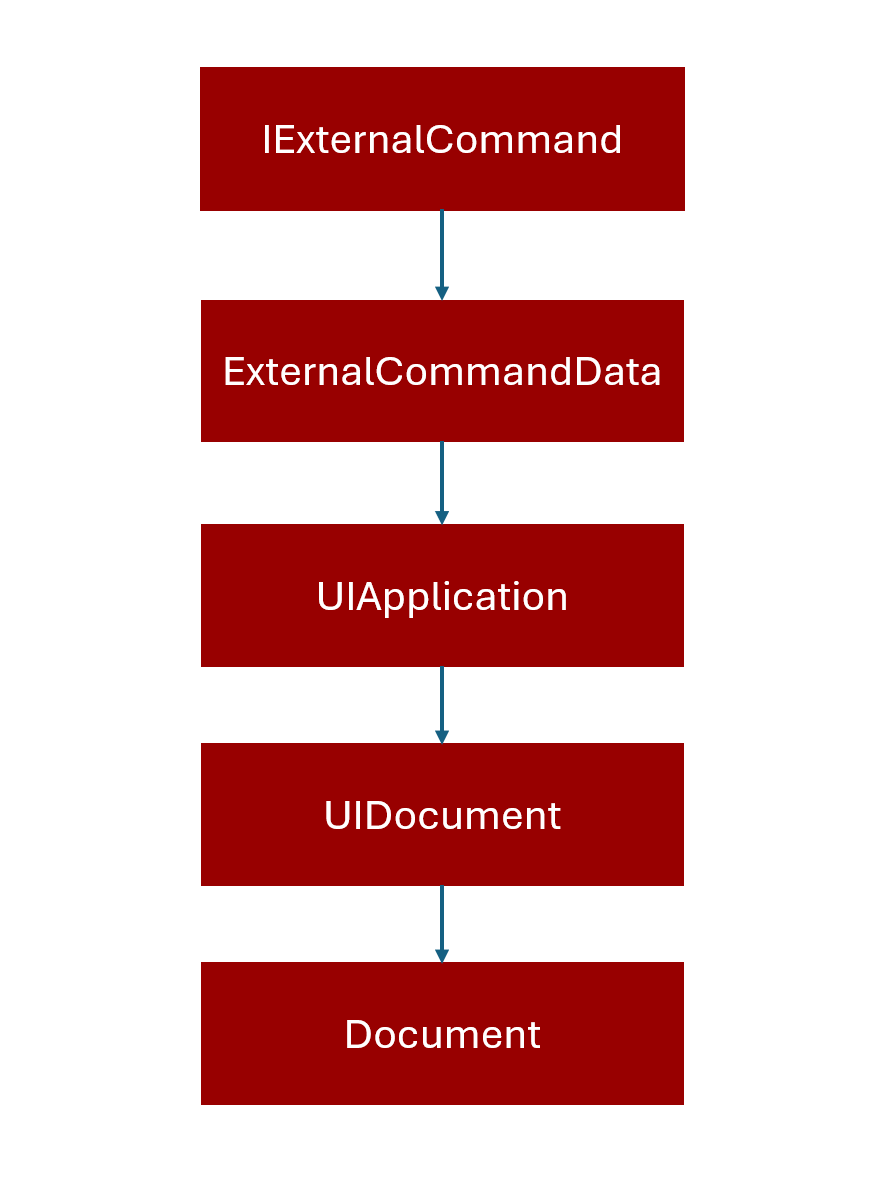
The Revit API is designed in a layered structure that starts from external commands and goes deeper into the Revit model. This structure ensures that developers can access Revit’s core functionality in a controlled and organized way.
External Command (IExternalCommand)
This is the entry point for any custom tool or plugin you create. When you run your command in Revit, the API calls the Execute() method of your class that implements IExternalCommand.
Key role: Defines what your add-in will do when triggered.
ExternalCommandData
Inside Execute(), you receive an ExternalCommandData object. This object provides essential context about the current Revit session, such as:
- Application: The Revit instance running your command.
- Document: The active project file you are working on.
- View: The current view displayed to the user.
UIApplication & UIDocument
From ExternalCommandData.Application, you get a UIApplication object, which represents the Revit application.
UIApplication.ActiveUIDocument gives you a UIDocument object, which represents the user interface document (the open project in Revit).
Why important? UIDocument allows you to interact with the user interface, select elements, and manage views.
Document
From UIDocument.Document, you get the core Document object. This is the main gateway to the Revit model data. Through Document, you can:
- Access elements (walls, doors, windows, etc.)
- Modify the model
- Create new elements
- Manage transactions (every change in Revit must happen inside a transaction)
In short
Sample Code:
using Autodesk.Revit.UI;
using Autodesk.Revit.DB;
using Autodesk.Revit.Attributes;
[Transaction(TransactionMode.Manual)]
public class MyFirstCommand : IExternalCommand
{
public Result Execute(
ExternalCommandData commandData,
ref string message,
ElementSet elements)
{
// Get UIApplication
UIApplication uiApp = commandData.Application;
// Get UIDocument
UIDocument uiDoc = uiApp.ActiveUIDocument;
// Get Document
Document doc = uiDoc.Document;
// Example: Show the document title
TaskDialog.Show("Revit API", $"Active Document: {doc.Title}");
return Result.Succeeded;
}
}Why This Architecture Matters
This layered design ensures:
- Security: Only authorized operations can modify the model.
- Stability: Changes happen in controlled transactions.
- Flexibility: Developers can access both UI-level and model-level data.
Conclusion
The Revit API opens up endless possibilities for customizing and automating your design workflow. By understanding its architecture—from IExternalCommand down to Document—you gain the ability to interact directly with Revit’s core model and user interface. Whether you want to automate repetitive tasks, create custom tools, or develop innovative plugins, mastering the Revit API will help you transform Revit into a powerful, tailored solution for your projects. With the right tools and knowledge, you can take full control of your design process and significantly boost productivity.