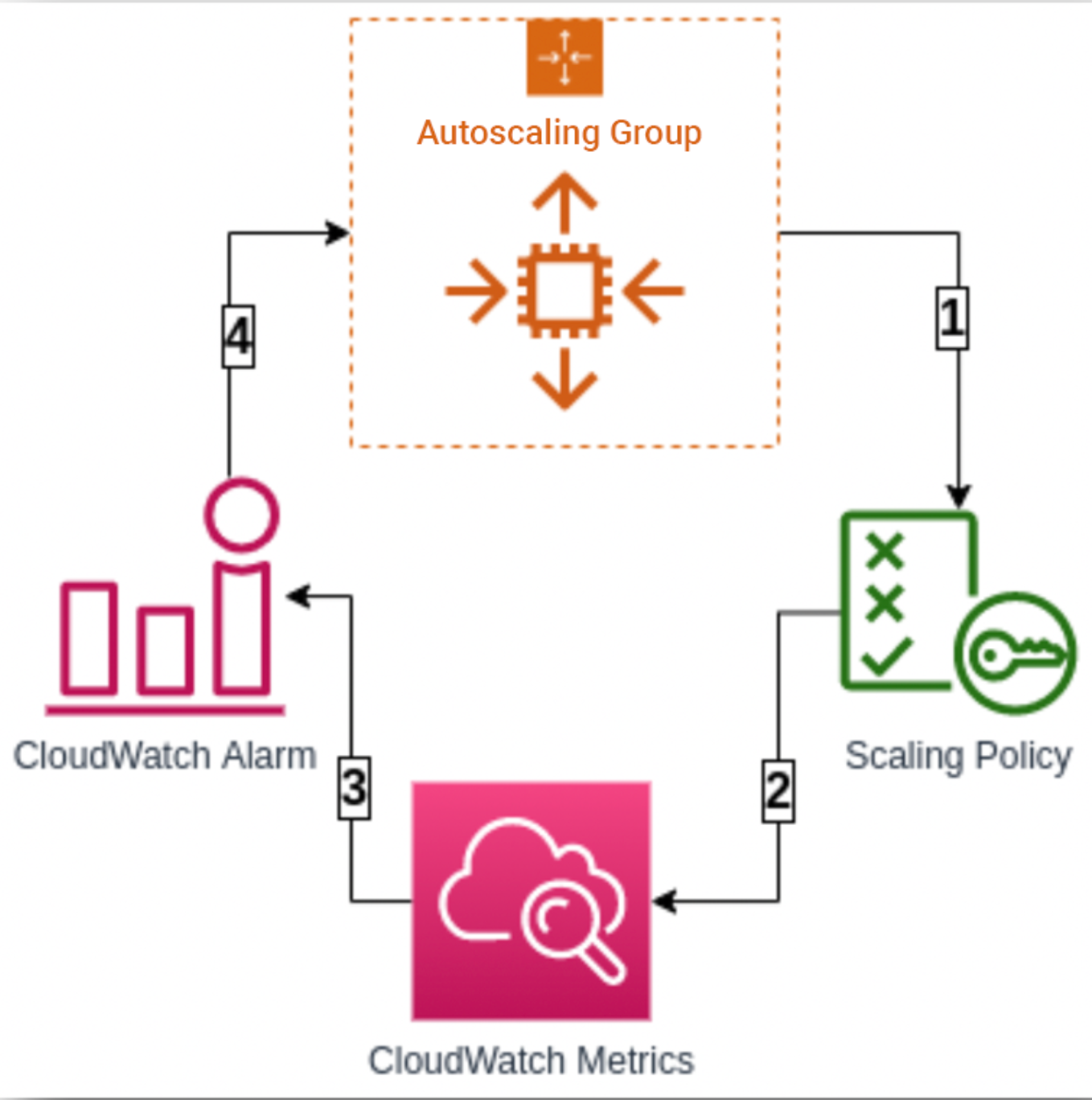
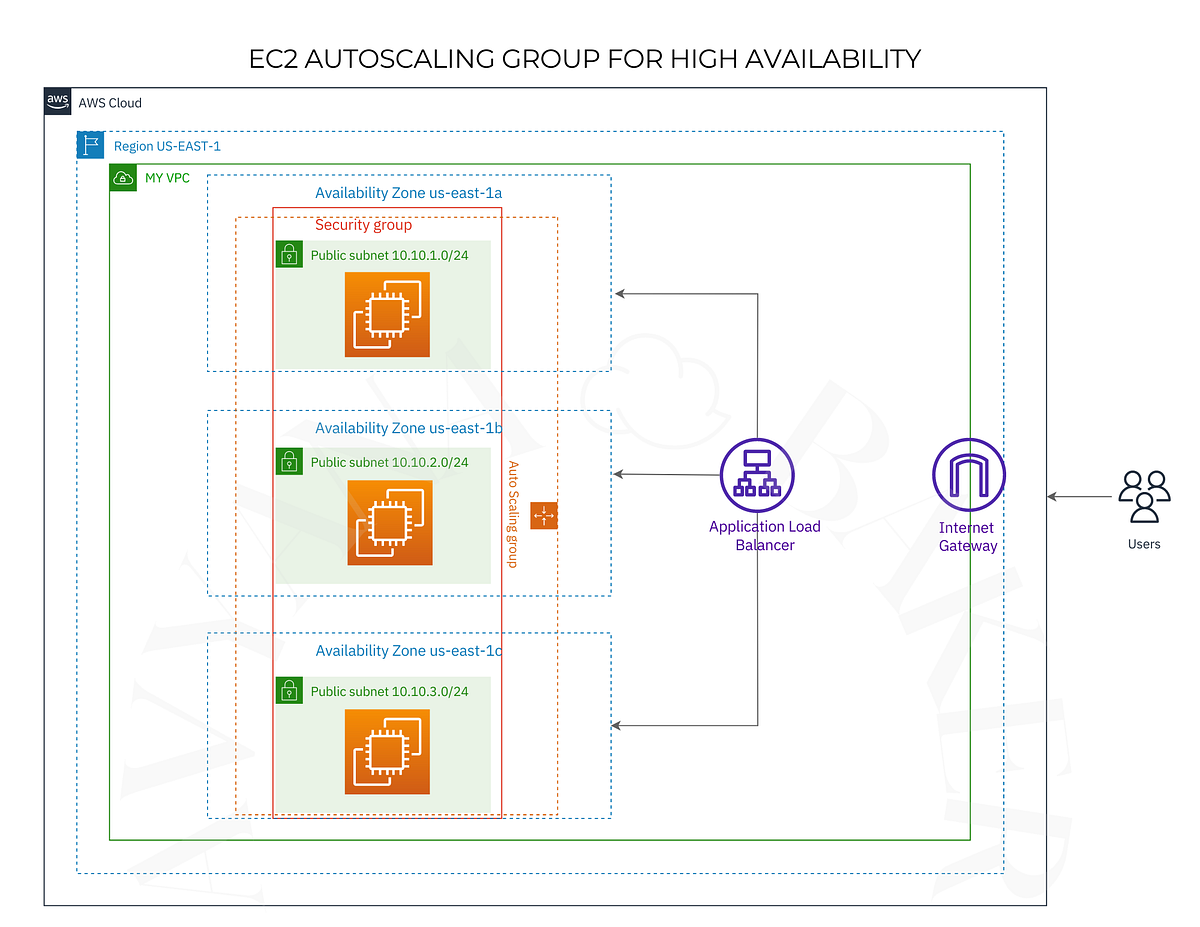
Auto Scaling Groups (ASGs) are a cornerstone of resilient cloud architecture. They allow your infrastructure to dynamically respond to load by adding or removing EC2 instances. In this blog, we’ll explore how to configure Step Scaling Policies using Terraform, triggered by multiple CloudWatch alarms—CPU, memory, and response time.
This setup is ideal for production environments where scaling decisions depend on more than just CPU usage.
What Is Step Scaling?
Step Scaling allows you to define scaling adjustments based on the magnitude of the metric breach. For example, if CPU usage exceeds 50%, you might add 1 instance; if it exceeds 80%, you might add 2.
Unlike Target Tracking, Step Scaling gives you fine-grained control over how your ASG reacts to different thresholds.
Terraform Setup Overview
We’ll define:
- An Auto Scaling Group (
example) - Three Step Scaling policies:
- Scale out on CPU
- Scale out on Memory
- Scale out on Target Response Time
- Three CloudWatch alarms to trigger these policies
Constants
locals {
asg_name = "example"
tg_arn_suffix = "example/c403f9a1ff6c8e8d"
lb_arn_suffix = "app/example/c3b1a1ddcd352e90"
}
These constants are used to reference your ASG, Target Group, and Load Balancer in CloudWatch alarms.
Step Scaling Policies
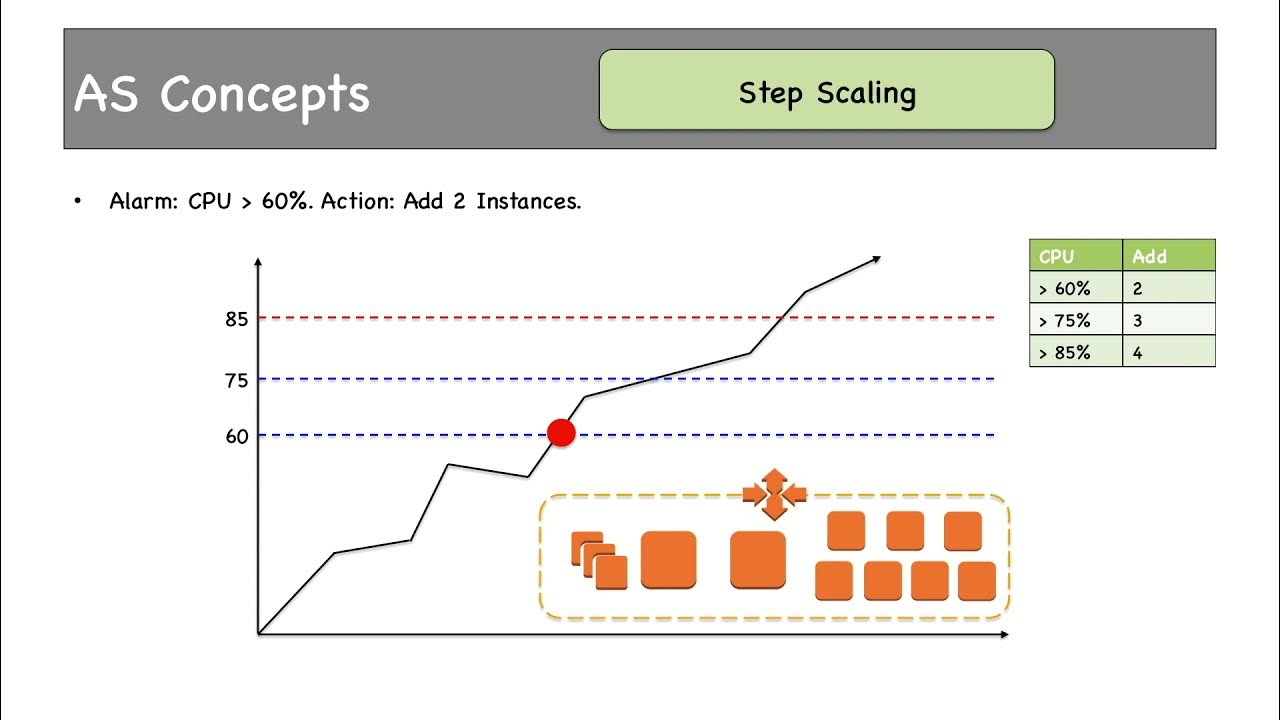
Each policy increases capacity by +1 instance when triggered.
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "scale_out_cpu" {
name = "example-scale-out-cpu"
autoscaling_group_name = local.asg_name
policy_type = "StepScaling"
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
metric_aggregation_type = "Average"
estimated_instance_warmup = 60
step_adjustment {
scaling_adjustment = 1
metric_interval_lower_bound = 0
}
}
Repeat similarly for memory and response time:
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "scale_out_mem" { ... }
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "scale_out_rt" { ... }
CloudWatch Alarms
1. CPU Utilization > 50%
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "cpu_high" {
alarm_name = "example-scaling-cpu-utilization-high"
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanOrEqualToThreshold"
evaluation_periods = 1
period = 60
statistic = "Average"
threshold = 50
namespace = "AWS/EC2"
metric_name = "CPUUtilization"
alarm_actions = [aws_autoscaling_policy.scale_out_cpu.arn]
dimensions = {
AutoScalingGroupName = local.asg_name
}
}
2. Memory Used Percent > 80%
This uses CWAgent metrics:
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "mem_high" {
alarm_name = "example-scaling-memory-used-percent-high"
namespace = "CWAgent"
metric_name = "mem_used_percent"
threshold = 80
alarm_actions = [aws_autoscaling_policy.scale_out_mem.arn]
dimensions = {
AutoScalingGroupName = local.asg_name
}
}
? Tip: Ensure your EC2 instances are running the CloudWatch Agent and publishing mem_used_percent.3. Target Response Time > 1s
This monitors ALB latency:
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "rt_high" {
alarm_name = "example-scaling-target-response-time-high"
namespace = "AWS/ApplicationELB"
metric_name = "TargetResponseTime"
threshold = 1
alarm_actions = [aws_autoscaling_policy.scale_out_rt.arn]
dimensions = {
LoadBalancer = local.lb_arn_suffix
}
}
Testing Your Setup
Once deployed, simulate load using tools like:
stress-ngorddfor CPUmemtesterfor memorywrkorabfor HTTP latency
Watch your ASG scale out in response to alarms.
Clean Up
To destroy the setup:
terraform destroy
Make sure you understand the dependencies between ASG, alarms, and policies before tearing down.
Final Thoughts
This multi-metric scaling strategy ensures your infrastructure responds to real-world bottlenecks, not just CPU. By combining Step Scaling with CloudWatch alarms, you gain precise control over how and when your services scale.
Using Terraform makes this setup reproducible and version-controlled—perfect for teams managing infrastructure as code.