What is Scrum velocity?
Scrum velocity is a critical metric in Agile project management. It measures the amount of work a Scrum team can complete during a single sprint, expressed in story points, hours, or a similar unit.
By tracking velocity over several sprints, teams can predict how much work they can realistically accomplish in future sprints, helping with planning and commitment.
For instance
- If a team completes 40 story points(*) in Sprint 1, 35 in Sprint 2, and 45 in Sprint 3, their average velocity might be around 40 story points per sprint.
(*): effort units. There are units of measurement used to estimate the effort required to complete a story.
Why Scrum velocity is useful?
-Predictability: It helps forecast the amount of work a team can complete in future sprints.
-Capacity Planning: Teams can use velocity to plan how much work they can realistically commit to in upcoming sprints.
-Improvement Tracking: It allows teams to assess their productivity and identify areas for improvement.
How do I calculate scrum velocity?

Calculating Scrum velocity is straightforward and involves the following steps:
- Identify Completed Work: At the end of a sprint, sum up the story points (or whatever unit of work your team uses) for all the tasks that were fully completed. Only count tasks that meet the "definition of done."
- Repeat for Multiple Sprints: Track the total completed story points for at least 3–5 sprints. This gives a more reliable average.
- Calculate the Average: Add up the total completed points across those sprints and divide by the number of sprints.
For example
- Step 1 & Step 2: Identify Completed Work and Repeat for Multiple
- Sprint 1: 30 story points completed
- Sprint 2: 28 story points completed
- Sprint 3: 32 story points completed
- Step 3: Calculate the Average-Average Velocity = (30 + 28 + 32) / 3 = 30 story points per sprint
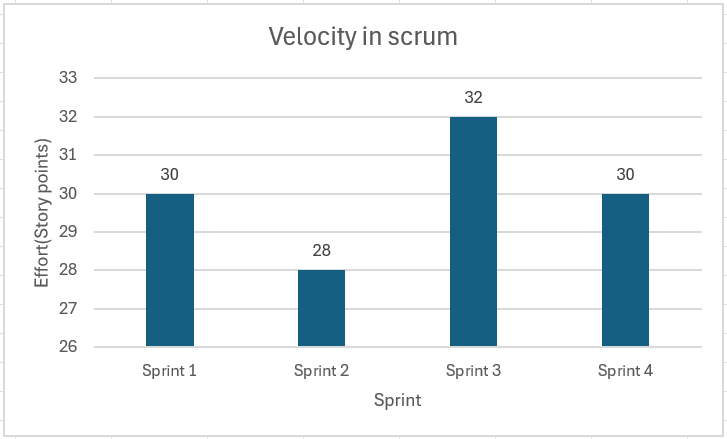
This average velocity helps your team predict how much work they can commit to in future sprints.
How can I improve my team's scrum velocity?
- Refine User Stories
Ensure user stories are clear, concise, and well-defined.
Break large tasks into smaller, manageable ones to reduce complexity. - Focus on Team Collaboration
Encourage open communication during daily stand-ups and planning sessions.
Build a cohesive team culture where members support each other. - Prioritize Retrospectives
After each sprint, hold retrospectives to identify what's working and what needs improvement.
Implement actionable changes based on retrospective feedback. - Optimize Workflows
Identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in your process.
Use tools like Kanban boards to visualize workflows and improve task management. - Avoid Overloading
Don’t overcommit to tasks in a sprint. It's better to focus on fewer items and complete them effectively.
Respect the team’s capacity and account for unforeseen challenges. - Upskill Team Members
Provide training or learning opportunities to enhance skills relevant to the tasks at hand.
Encourage cross-functional collaboration to make the team more versatile. - Foster Continuous Improvement
Celebrate small wins to boost morale.
Use metrics, like velocity trends, as feedback—not as a pressure tool.
Keep in mind!!!

Velocity is a team-specific measure, so it’s best not to compare it between teams.
It’s also normal for velocity to fluctuate due to factors like team changes or varying task complexity.