Security is an ambiguous term and concept since the borderline between security and risk often remains thin. Up to today, there has never been a concern about software being too secure, instead being invasive with the anxiety of being exposed to unknown cyber threats, unpatched system loopholes, and sudden compromised integrity.
Businesses have been attempting to set up their best defense system within the software core and the physical infrastructure. On a personal level, safeguarding your data may be typically simple. Many choose to secure their valuable photos, intellectual properties, memos, etc., by saving them onto a thumb drive that has been encrypted and kept in a location where only they can access the key.
However, companies and organizations have to deal with data protection on a much larger scale as their business expands. Their company’s private data includes product prototypes, customer and employee confidential information, ideas, research, and experiments, generally valuable intangible assets. As well as the tangible resources we typically think of, such as hardware and software, the tools that enable companies to work with and store their data.
While there are security strategies and technological solutions that can help, the CIA Triad is the key concept that underpins them all, serving as a guide for protection measures, controls, and overall strategy.
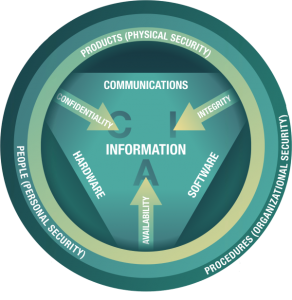
What is the CIA Triad?
The CIA triad is widely recognized as a fundamental model in the information security system. Rather than being a singular doctrine created by a single author, it has evolved and drawn concepts from various sources, some of which are as old as modern computing.
The word itself is the self-indication of what CIA means. It is the abbreviation of the three primary components in security protection: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, which acts as the foundation for developing security systems in identifying vulnerabilities and figuring out the solutions to solving such.
The CIA triad has been referred to in both ISO 27001 as well as the GDPR as the important principle to shape organizations’ security standards the right way. Once the three focal points have been met, the organization can likely handle threat incidents more effectively and accurately.
Understanding the three principles of the CIA Triad
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is synonymous with privacy and involves implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. This may include, but is not limited to, financial records, business plans, personally identifiable information (PII) such as Social Security Numbers (SSNs) or dates of birth, email records, payment information (including credit/debit cards), password-protected records, and protected health records.
To effectively protect data, it is common practice to categorize it based on the potential harm that could result from it being accessed by unauthorized parties. Based on these categories, more or less strict security measures can be implemented accordingly.
There are several ways to establish data confidentiality, such as implementing access control lists, encrypting volumes and files, setting file permissions, role-based access control (RBAC), encrypting data during processing, transfer, and storage, enabling remote wipe capabilities, and providing education and training to all individuals who have access to confidential data.
Integrity
Integrity involves maintaining data’s accuracy, consistency, and trustworthiness over its entire lifecycle. Data must not be altered during transit, and steps must be taken to prevent unauthorized individuals from modifying it.
Data integrity can be preserved through various methods such as encryption, auditing, version control, digital signatures, digital certificates, intrusion detection systems, hashing, authentication, and access controls. These methods are designed to maintain data accuracy, consistency, and reliability throughout its lifecycle and to prevent unauthorized changes or access.
Availability
Availability means information should be consistently and quickly accessed when needed by authorized parties. This involves proper maintenance of hardware, technical infrastructure, and systems that store and display the information.
In order to ensure that your data systems remain available on demand, a variety of potential challenges must be taken into account, including human error, hardware and software failures, network disruptions, power outages, natural disasters, and cyberattacks.
Some methods used to guarantee data and application availability include fault tolerance (hardware), redundancy (networks, applications, servers, and services), regular software patching, system upgrades, disaster recovery, and maintaining backups and backup copies.
What is the importance of the CIA Triad?
The CIA triad comprises three inseparable and interconnected components to establish safety policies and systems within organizations. It is a comprehensive checklist for safeguarding data against rising cyber threats. Failure to adequately implement one or more of these principles is considered a security compromise. By following the CIA triad, organizations can enhance their security posture, maintain compliance with regulations, and ensure business continuity, making it an essential aspect of information defense.
What is the most important part of the CIA Triad?
The importance of each of the CIA triad principles – confidentiality, integrity, and availability – may vary depending on an organization’s security objectives, regulatory requirements, industry, or business nature. For instance, integrity may be more important than confidentiality and availability in government agencies or financial institutions. On the other hand, data availability is crucial in the e-commerce and healthcare sectors. However, there may be a trade-off in prioritizing one of the principles over others.
What are the challenges for the CIA triad?
The CIA paradigm faces challenges with big data due to the large amount of information organizations must protect, the various sources from which data is collected, and the multiple formats in which it is stored. The costs associated with managing duplicate data sets and implementing disaster recovery plans can also be substantial. Moreover, since the primary focus of big data is collecting and analyzing large amounts of information, adequate oversight should be noticed.
Internet of Things security is also challenging because IoT consists of many internet-enabled devices other than computers, which may need to be regularly updated with safety patches and are often configured with weak or default passwords. If left unprotected, IoT could be used as a separate attack vector or to create a “thing bot.”
As more and more products are developed with the capacity to be networked, it is crucial to prioritize security during product development.
Conclusion
The critical defense components of the CIA triad are Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. When businesses establish a security agenda for data protection, the CIA Triad becomes a valuable tool to gauge the necessity of implementing security controls. By implementing these principles seriously in practice, businesses can effectively and consistently assess their business-associated risks, evaluate them properly, and safeguard their data at the baseline.
ContactContact
Stay in touch with Us





